Categorization:Harness Component
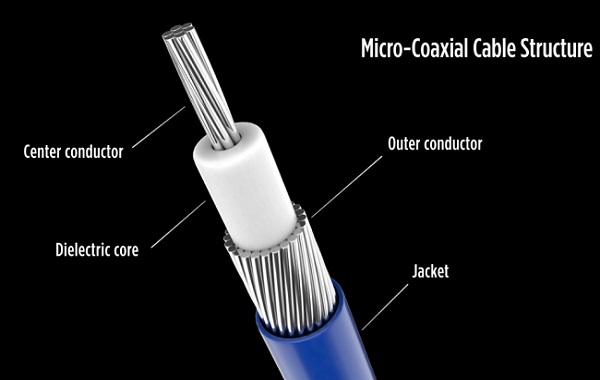
Part 1: Frequency Range and Limitations of Ultra-Fine Coaxial Beam
The available frequency range of ultra-fine coaxial cable束 is not fixed, but is determined by the cable diameter, medium material, shielding structure, and connector performance. Its typical working range covers from basic signals at low frequencies to several hundred MHz, up to common ranges of several hundred MHz to several GHz, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G Sub-6G, MIPI, and eDP. For more advanced millimeter waves and high-speed test interfaces, by optimizing the medium, structure, and technology, ultra-fine coaxial cables can also support frequencies above 10 GHz. However, the higher the frequency and the finer the wire, the more obvious the loss, so in actual applications, it is often necessary to keep the cable length as short as possible to reduce insertion loss and phase distortion.
Factors affecting high-frequency performance of structures and materials
The performance of the same ultra-thin coaxial cable varies significantly due to differences in materials and processes. The dielectric constant and loss tangent of the medium material determine the signal attenuation level at high frequencies; the finer the conductor, the stronger the impact of the skin effect, especially at GHz levels. Inadequate shielding layer weave density may also cause leakage and crosstalk. Additionally, the reflectivity of the connector, parasitic parameters, and transition structures have a huge impact on the overall frequency capability. Moreover, excessive cable length can lead to standing waves, phase shift, and other issues, thus, the higher the frequency, the stricter the consistency requirements for materials, structure, and technology.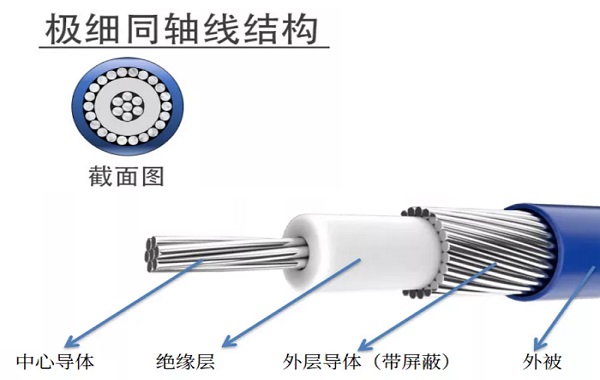
Three, realize the matching and verification strategy with excellent performance
In high-speed differential signal or radio frequency chains, to achieve ideal performance, matching design is crucial. It is essential to ensure that the entire chain maintains consistent impedance (50 Ω or 100 Ω) and strictly control the length errors between differential pairs to avoid phase mismatch causing eye diagram shrinkage. The shielding layer should be continuous and stablely grounded to reduce interference coupling. In connector selection, appropriate small high-speed interfaces matching the target frequency band, such as I-PEX, MHF series, etc., should be chosen. After the design is completed, it is also necessary to verify key indicators such as insertion loss, return loss, S parameters, and eye diagrams through simulation and actual testing to ensure that the final chain meets the frequency requirements.
I amSuzhou Huichengyuan Electronic Technology, long-term focused on the design and customization of high-speed cable harnesses and ultra-thin coaxial cable harnesses, committed to providing stable and reliable high-speed interconnect solutions. If you have related needs or want to learn more, please contact Manager Zhang :18913228573 (WeChat number))。