Categorization:Harness Component
In high-speed interface design, multi-channel MIPI signals often need to be transmitted simultaneously, which is a very common situation in smartphone camera modules, AR/VR display modules, and industrial camera systems. However, as the number of channels increases, issues such as crosstalk, EMI (electromagnetic interference), and impedance discontinuity will be significantly amplified, eventually leading to pixelation, resolution decline, and even unstable operation of the link. So, how can engineers effectively cope with these challenges?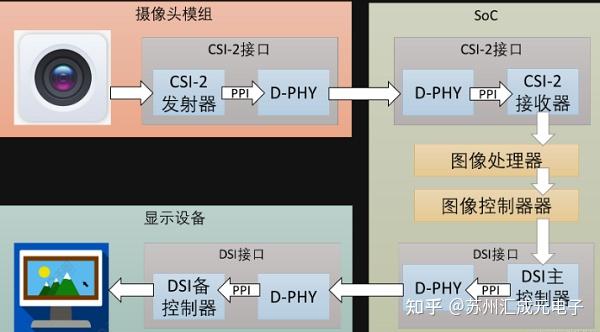
Optimize wiring and topology structure
In an early project, we encountered a typical crosstalk problem: multiple MIPI signals were routed in parallel on the PCB, resulting in serious distortion of the waveforms. Later, by increasing the routing spacing, adjusting the layer structure, and avoiding excessively long parallel routing, the problem was significantly improved. Especially, maintaining consistent differential pair spacing was very significant for improving signal integrity. This experience also indicates that in MIPI high-speed design, a reasonable routing topology is often the first line of defense.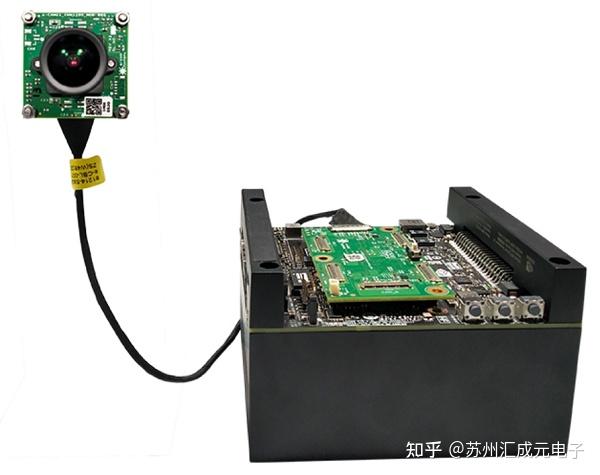
Two, introducing shielding and ultra-fine coaxial cables
Relying solely on PCB optimization is sometimes not enough, especially in the connection parts between modules and mainboards. We have tried to use extremely thin coaxial cables (Micro Coaxial Cable) for signal transmission, whose shielding layer can not only effectively reduce cross-talk between channels but also significantly enhance the ability to resist external EMI. This solution has already become quite mature in multi-channel MIPI camera modules.
In addition, shielding structure and grounding design are also crucial. In practice, we have found that adopting a multi-point grounding strategy can effectively cut off interference paths and prevent the occurrence of "cross talk" between different channels.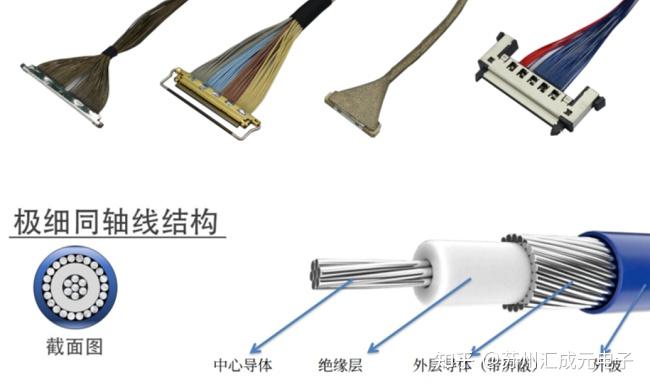
Three, impedance control and interface matching
MIPI interface has very strict requirements for impedance matching. We once found in a long-distance transmission test that due to the mismatch of connector and cable impedance, serious signal reflection occurred. Subsequently, we replaced it with the I-PEX connector with more precise impedance matching and added matching resistors at the driving end, and only then was the signal integrity restored. For longer-distance applications, retimer or equalizer chips can be introduced for compensation to further stabilize the transmission performance.
Four, comprehensive system design
Multi-path MIPI signal interference issues are often not caused by a single factor but rather the result of systematic coupling. During the design phase, several key aspects should be considered comprehensively:
4.1 Interface standard and protocol selection
4.2 PCB wiring rules and impedance control
4.3 Reasonable Application of Ultra-fine Coaxial Cable (Micro Coax)
4.4 Shielding layer and grounding design
4.5 Connector and circuit matching.
Only by systematically integrating these links together can the stable and reliable transmission of high-speed signals truly be achieved.
The handling of multi-channel MIPI signal interference not only tests the circuit design capability, but also challenges the system architecture level. From wiring, shielding to interface selection, every detail may determine the final image quality and stability. Practice has proven that introducing ultra-fine coaxial cables and other high-performance cable solutions often plays a decisive role in critical links.
I am[Suzhou Huichengyuan Electronic], Focuses on the research and development and customization of high-speed cable harnesses and ultra-fine coaxial cable harnesses, committed to providing customers with high stability and high reliability high-speed interconnect solutions. If you are looking for a better signal cable harness solution, welcome to contact:Manager Zhang 18913228573 (WeChat number the same)。