Categorization:Product Information
With the development of power communications, more and more fiber optic cables are used in power communication lines, the current domestic use of more ADSS, OPGW cable. In recent years, the application of ADSS fiber optic cable has some problems, the operation of the interruption of cable and other accidents have occurred repeatedly. This paper discusses the design, selection, construction and maintenance of ADSS, hoping to help the majority of power communication users.

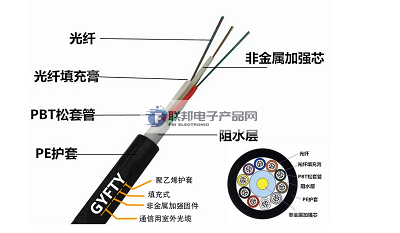
First, the design and selection of ADSS fiber optic cable In addition to the design of optical units, the design of ADSS fiber optic cable mainly consider the mechanical strength and the outer sheath of the galvanic corrosion problem.ADSS fiber optic cable for the full self-supporting type, requires very good mechanical properties, which is mainly through the addition of aramid yarn to ensure. In the design, we must consider the power line stall distance and the installation of the arc of the cable, and then according to the installation of regional climatic conditions, such as wind load, ice load calculated the mechanical strength requirements of the cable, and then projected the amount of aramid. ADSS cable design life of more than 20 years, so in the design of the cable, but also to consider that in the long term use of fiber optic cables on the cable may be attached to the dirt to increase the load. Mechanical strength can be shown mainly through the tensile window indicator, that is, the cable is subjected to extend how much when the fiber begins to strain. The use of large spans requires ADSS cables than ordinary cables have a larger tensile window, but this indicator is too large will lead to fiber optic micro-bending loss, practice shows that the mechanical strength control at 0.8% up and down is more appropriate. In the high-voltage conductor around the ADSS cable and the phase line, the potential generated by the capacitive coupling between the ground in the wet surface of the cable will produce leakage current; when the surface of the cable is dry, it will be in the dry area of the arc, resulting in heat erosion of the outer sheath resulting in cracks, and in serious cases, the cable will be fractured resulting in communication accidents. At present, there have been many incidents of cable breakage in the country, especially in the 110kV line cable without the use of AT sheath material and the use of non-full-media cable is more likely to occur. At present, the use of AT material ADSS fiber optic cable can not be greater than 25kV induced potential environment, manufacturers should control the process, so that the outer sheath is smooth, rounded. On the choice of ADSS fiber optic cable, many users encountered a problem is to choose the center tube cable or stranded fiber optic cable. Center tube cable has a small outer diameter, light weight advantages, but compared to the stranded cable difficult to obtain a large tensile window, while the cable's bending performance is slightly worse, so the ADSS cable using stranded type is better. Some users in the selection of fiber optic cables pay more attention to the price of the product, the amount of material and ignored the enterprise's ability to control the process and fiber optic cables and power lines with. Many users will require manufacturers to use a certain brand of aramid yarn and even specify the use of how many roots, while different manufacturers use the same number of aramid yarn to achieve mechanical strength is different, which is due to the manufacturer's ability to control the application of process control caused by the high and low. Aramid yarn casting process must ensure that the aramid in the fiber optic cable in a straight and no pre-stretch state, while all the aramid in the fiber optic cable uniform force, so as to achieve the ideal tensile strength. In the mechanical strength index design must be projected back to the tower force situation, power line tower in the design did not consider hanging ADSS fiber optic cable, so should pay full attention to the fiber optic cable tower impact, to ensure line safety. In addition, for the application of voltage levels to emphasize one point: 110kV lines should be used AT sheath cable, 220kV or more power lines should not be used ADSS fiber optic cable. Second, the construction and maintenance of ADSS cable ADSS cable construction quality and maintenance quality of good and bad on the operation of the cable has a great impact on the current actual situation of some irregularities, the following points are worth noting. 1. construction preparation (1), the cable appearance check: the user receives the cable should be checked in a timely manner after the cable disk and the outer layer of the cable, to determine that the received cable is not damaged; check the center of the cable disk holes have no damage to the outer sheath of the cable or impede the optical cable, the outer sheath of the cable or impede the safety of optical cable. Check whether the center hole of the cable tray has any damage to the outer sheath of the cable or any obstacle that prevents the fiber optic cable from being rolled up and unfolded. (2) Quantity check: check the total number of fiber optic cables and whether the length of each disk is consistent with the contract requirements. (3), quality inspection: optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) to check whether the cable has been damaged during transportation, the data obtained from the inspection can be used to compare with the acceptance test data after installation, and can be used as part of the data record, which will help in emergency repair work in the future. (4), the installation of the metal check: the installation of the required metal type, number of inventory, if not in line with the contract requirements should immediately contact the supplier manufacturers, before the actual construction properly resolved. 2. Installation Precautions (1) installation of fiber optic cables should ensure that the minimum bending radius (dynamic for the cable OD 20 times, static for the cable OD 10 times); at the same time, in the whole process of installation of fiber optic cables can not be twisted or compressed; the cable is subjected to a minimum bending radius (dynamic for the cable 20 times, the cable OD 10 times); the cable can not be twisted or compressed; the cable is subjected to the or pressure; cable tension should not exceed the range provided by the manufacturer of the arc droop and tension table. (2) The design of ADSS fiber optic cable suspension point to consider the following factors: field strength distribution, the minimum distance from the ground, the minimum distance from the conductor, etc., at the same time, the actual installation work should be strictly in accordance with the selected point of operation in order to protect the safety of the fiber optic cable. (3) traction, tension, temporary positioning bar, fusion splicing and other locations must consider the design, logistics and equipment and other factors. In the fixed cable tray construction, the cable must be divided into several sections of release, the length of each section depends on the location of the fusion splicing point, whether the vehicle can pass through, whether the equipment installation is feasible, obstacles, the length of the cable tray, etc., at the same time, it is also necessary to consider the cable's greater installation of tension, towers and other factors such as the tension of the greater load. (4) Selection of traction machine and tension machine relative to the position of the tower, can not make the tower load overload, also can not make the fiber optic cable by the tension is too large. Traction machine to the tower distance should be 4 ~ 5 times the height of the tower, so that the fiber optic cable, pulley and tower load is small. ANSI/IEEE 524 provides for the setup of a temporary sling to prevent overloading of the tower. The tensioner and cable tray bracket must be in a straight line with the two nearest towers to prevent the fiber optic cable from twisting and wear on the fiber optic cable from both sides of the pulley. (5) The application of temporary positioning rods and fixtures is determined by the size of the expected load tension of the fiber optic cable, and the influence of wind vibration should be considered when selecting fixtures. When adjusting the arc sag of the fiber optic cable, a temporary downward sling should be installed to prevent structural imbalance, when the temporary positioning bar distance from the tower should be not less than 2 times the tower height. Before installing the fiber optic cable, all temporary slings should be tightened. (6) When the installation route crosses roads, highways, railroads and transmission lines, some support facilities should be added to ensure the safety of the fiber optic cable. When working in cross terrain, the field personnel should keep in touch with the tractor and tensioner operators. (7) The terrain of each traction section should be analyzed to ensure the safe conduct of construction. If obstacles are encountered during construction, the fiber optic cables should not be dragged or made to directly touch the obstacles to avoid damage to the outer sheath of the fiber optic cables. (8) In order to construct safely and effectively, it is recommended to release the cable at a speed of about 3km/h. Release the cable should maintain a balanced speed, the traction process, the tension machine operator should pay attention to the traction tension can not exceed the requirements of the greater tension, it is recommended that the traction force does not exceed half of the tension in the initial arc sag. Due to the length of the cable, the number of pulleys used, route changes and tower elevation changes, etc., in the application of larger spans of cable may require a larger tension, which should be particularly careful, because this time the tension at the traction end is much larger than the value shown on the tensiometer. In order to prevent the rotating speed of the cable disk too fast, the rotating shaft of the cable disk should be applied to a small but smooth reverse force. When the cable will be released, the reverse force should be reduced in time, because at this time the tension on the fiber optic cable will increase. (9) in the optical cable fusion, to leave enough cable and fiber length for fusion, cable length should be able to lead down from the tower to the fusion point. Fiber optic cable splicing should be completed on the ground and should not be in the air. Fusion after the cable should exist in the junction box placed in the tower or buried in the ground, the cable end should be closed to tape to block the water. 3. construction records and document preservation of complete records is the necessary guarantee of normal communication work. As the fiber optic cable communication involves the design, construction, operation and maintenance of many departments, after the completion of construction, each department should collaborate with each other, all records are properly preserved for future work. The record documents should include the following: (1) Topographic index map of the line. This map records the line and the roads it passes through, so that the locations to be reached can be found quickly in future work, and for joints, road or river crossings, they should all be labeled in the map. (2) Line composition diagram. The map includes the line in the joints, roads or river crossings and other places used in the optical fiber cable disk number, disk length, fiber type and number of cores. (3) Installation diagram. The diagram records the equipment at each tower and tower conditions and pole spacing, grounding and other conditions. (4) Fiber optic circuit diagram. The diagram indicates the actual fiber optic circuit, the number of cores used, the number of spare cores, the fiber optic color code and the handling of the fiber optic that occurs in the future. (5) Acceptance data records. Should record the acceptance of the measured input optical power, received optical power, attenuation and other data, in addition to optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) on each fiber (1310nm and 1550nm) measured graphs, fusion loss, connector insertion loss and fiber and pigtail photos. (6) Documents provided by the manufacturer, including data provided by the manufacturer for each fiber optic cable and the fibers in it, potential diagrams of different tower types calculated at the request of the user, and arc droop and tension tables. (7) Multiple copies of the original records shall be made and kept by both the construction and maintenance units, and one copy shall be available at the end point of the system. Records should be promptly revised after line modifications and emergency repairs, etc. have occurred. Unlike ordinary fiber optic cables, ADSS cables require close collaboration between users and manufacturers, and strict control of all aspects of design, production, construction and maintenance, etc. After meeting the above conditions, ADSS cables can be operated stably to ensure the long-term benefits of the electric power communication business.
2, on the federal electronic products network platform related to the introduction and sales of products brief: federal electronic products network - a professional agent / production / sales of all kinds of [connectors | wiring harness | wire and cable products]; if you have a related [connectors | wiring harness | wire and cable products] purchasing / sourcing needs or would like to buy / to understand which connectors | wiring harness | wire and cable products we can provide solutions, please contact our business staff below; If you have related [connectors | harness | wire and cable products] sales / resources and promotion needs, please click on the ¡¡ Business Cooperation ← ¡" and specialists to discuss!